CAPABILITIES
Boiler Corrosion Analysis
The two most common causes of internal boiler corrosion are:
a) Oxygen attack; or
b) Acid attack following chemical cleaning.
Their can be other types of corrosive attacks on the tubes such as caustic gouging which is related to hydrogen embrittlement, but these are often associated with other factors such as circulation deficiencies.
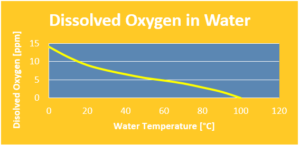
The primary means of removing oxygen from feedwater is by deaeration. The solubility of oxygen ( & CO2) reduces rapidly with rising water temperatures. Deaerators utilize this natural phenomena to remove oxygen (& CO2) from feedwater. A malfunctioning deaerator or an inadequate deaerator steam supply is a common cause of internal oxygen corrosion damage.
We have investigated many cases of internal corrosion damage caused by oxygen attack.

Typical corrosion scenario: Poor deaerator performance is the suspected cause of high feedwater oxygen levels. This requires the deaerator low pressure steam supply to be checked and verified.
A typical investigation may involve the following activities:
Site Visit & Testing:
- An inspection of deaerator internals and testing of the LP steam supply is required.
- A Design Boiler engineer would also be required to review the water treatment record in order to identify obvious anomalies. For example, increased use of sodium sulphite would indicate potential deficiencies in deaerator performance.
Computer Modelling:
- A heat balance of the LP steam system would be undertaken in order to identify any significant imbalances in the heat distribution within the steam cycle.
- Specific operating issues such as the requirement to dump surplus steam to prevent flashing within the deaerator would be investigated.
- The viability of possible remedial strategies would be evaluated and selected options would be submitted and discussed with the client.
More details of our capabilities in this field may be found here.
