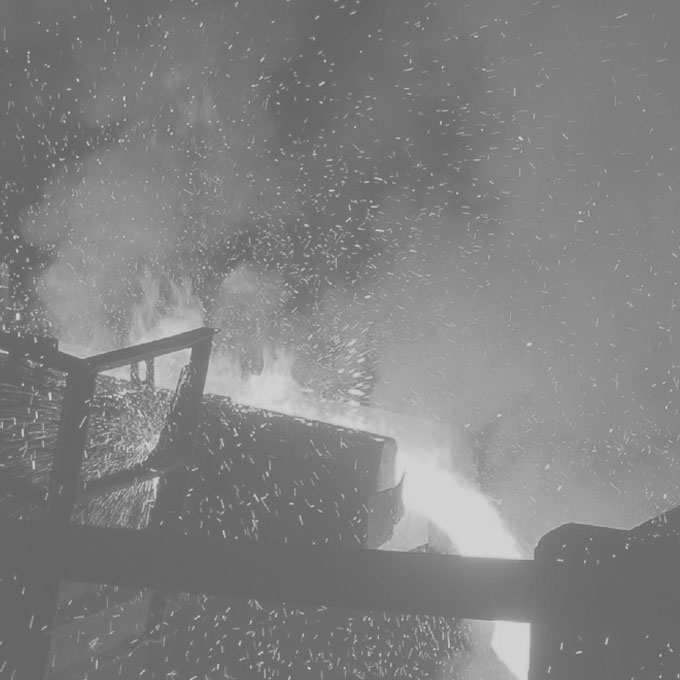
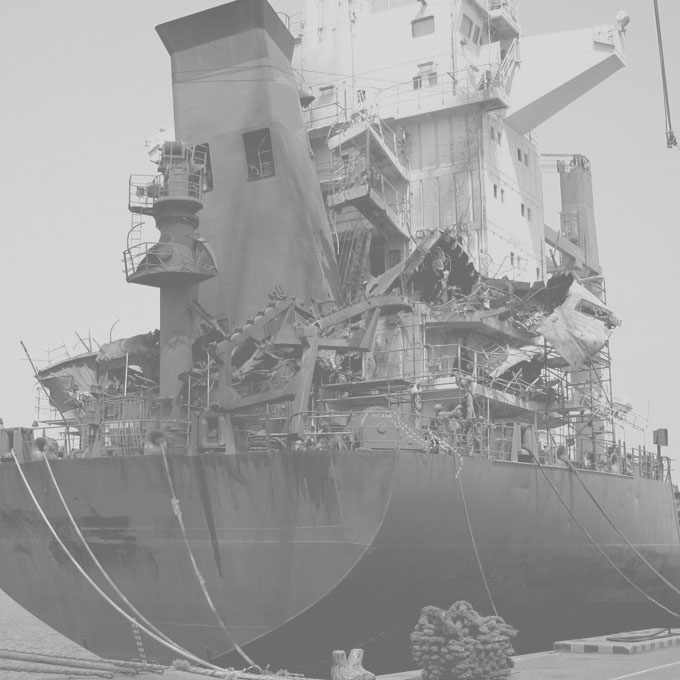
01 Airheater Metal Fire | Biomass Fuel
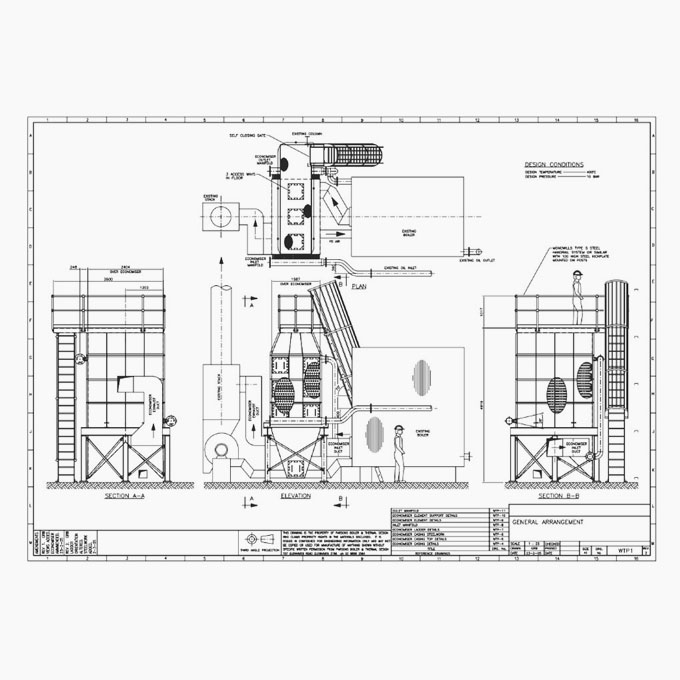
Design Boiler was engaged to investigate the cause of a metal fire in a wood fired boiler that had destroyed its airheater. The fire effectively shut the plant down for over 12 months. A metal fire is one of the most extreme operational hazards likely to be encountered within a boiler. Once initiated they can be extremely difficulty to extinguish and they have the capacity to destroy an entire boiler in a very short period of time.
02 Biomass | Hotwater Boiler Design
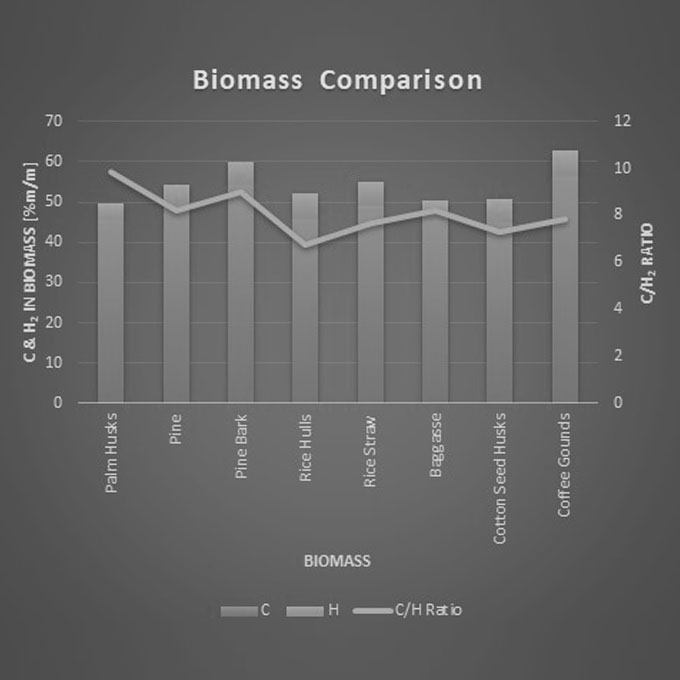
A small timber processing plant needed to reduce energy costs. Sawdust, which was a site waste product, was available as a free source of fuel. If this could be burned to heat hot water, it would displace Natural Gas, and reduce the site’s energy costs.
03 Biomass | High Particulate Emission & Load Limiting
A biofuel plant had purchased a 45 T/hr boiler from a leading boiler manufacturer to generate electricity through a small steam turbine at their production facility. However, the plant owners believed that the boiler was unable to achieve its Maximum Continuous Rating (MCR) and that its particulate emissions exceeded statutory limits. Design Boiler was engaged by the boiler manufacturer to provide an independent opinion.
04 Biomass | Thermal Oil Economiser
A medium sized timber processing plant was looking to expand its operation by introducing a new product. The production expansion was going to impose a significant additional burden on the site heat plant capacity. The site was remote with no reticulated gas supply available and the cheapest alternative fuel source was a bulk LPG which would have to be trucked in. A cost benefit analysis indicated that the cost of providing LPG as a substitute fuel source would render the proposed production expansion unviable.
05 Boiler Internal Corrosion
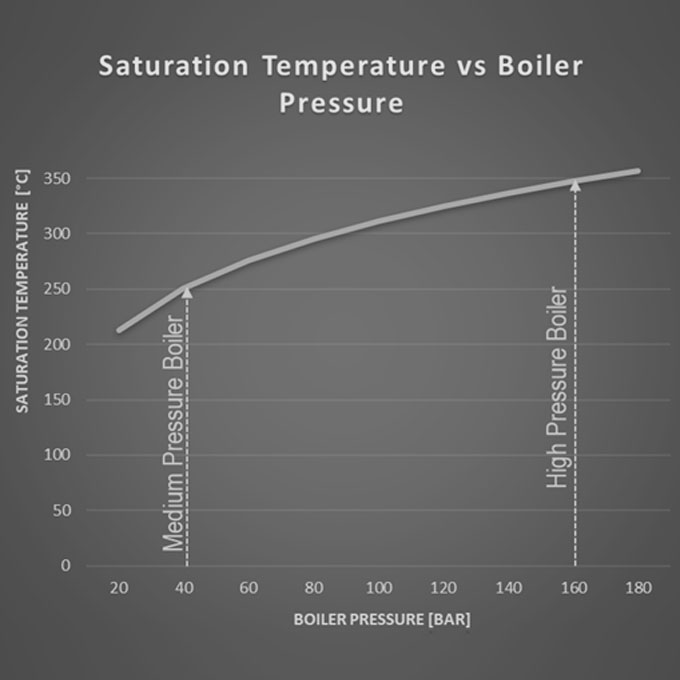
A relatively new high pressure boiler was installed on the deck of an oil tanker that had been recently converted to a Floating Production Storage & Offloading [FPSO] facility. The 110 [TPH] boiler operated at around 65 [Bar] and produced 510 [°C] superheated steam. Shortly after its 12 month warranty period had elapsed, and following a statutory boiler inspection, significant corrosion damage throughout the entire boiler was discovered.
06 Boiler Explosion
A small low pressure (8 [Bar]) waste heat recovery boiler installed at the back end of the main propulsion engine of a trading ship exploded at sea shortly after the boiler had been serviced. The explosion caused extensive damage to the ship and prevented it from sailing under its own power. It was towed to a nearby port where it was laid up for over 12 months for repair.
07 Boiler Vibration
A natural gas fired high pressure boiler recently installed in a gas refinery had been experiencing major vibration problems which limited the boiler’s ability to achieve its maximum rated output. As was typical of boiler vibration issues, the problem exhibited a threshold load below which the vibration did not occur.
08 Defective Boiler Circulation
A 600,000 [lbm/hr] high pressure pulverized coal boiler operating at a steelworks experienced persistent furnace wall tube blistering within 6 months of being first commissioned. After 3 months some of the blistered tubes began to fail causing frequent forced plant outages and expensive production losses. The boiler manufacturer blamed poor water treatment, pointing to the presence of a thin scale detected on the inside surface of the tube within the zone of the failures. A new water treatment chemical supplier was engaged but despite an intense focus on optimizing water chemistry over an additional 12-month period the problem persisted.
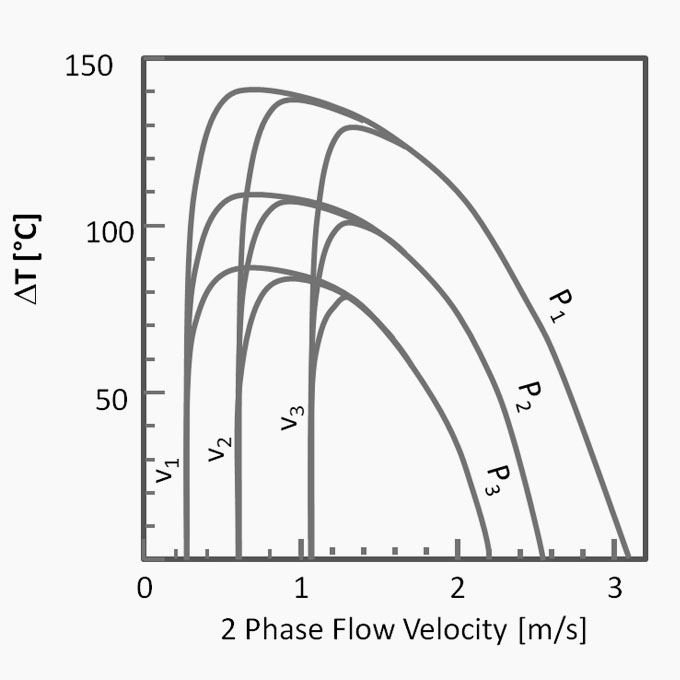
09 Downcomer Instability
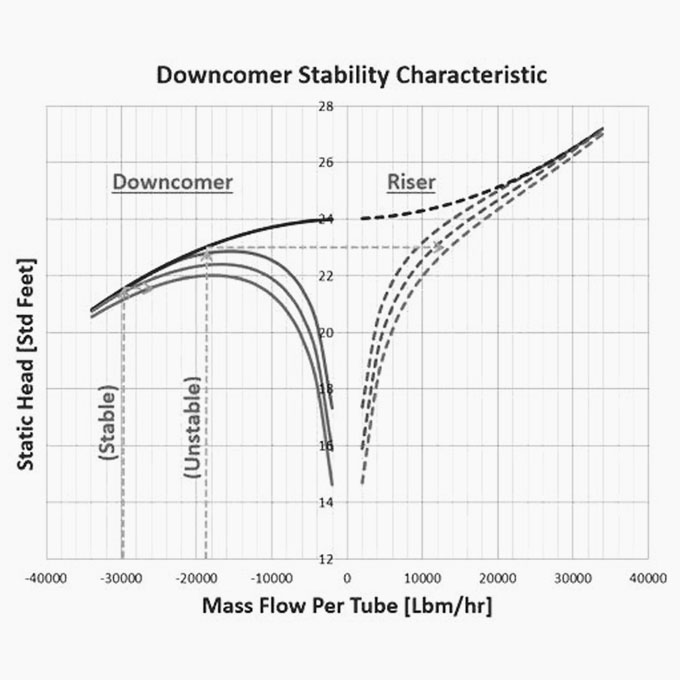
The commissioning of a new 250 [TPH] high pressure boiler could not be completed because of ongoing problems with the drum level control system. The boiler also exhibited a number of other unusual problems including a significant variation in drum level between the left and right hand side of the drum. The boiler was a pulverized coal fired natural circulating bi drum unit producing 62 [Bar] steam at [470] °C. It was fitted with a three-element drum level control system but irrespective of whatever control settings were made the drum level would initially exhibit a measure of stability only to become erratic and uncontrollable during subsequent operation.
10 Economiser Metal Fire
An exhaust gas boiler fitted in the uptake of a trading VLCC motor tanker was destroyed beyond repair by a metal fire, stranding the fully laden vessel in a foreign port. The high value of the cargo and the size of the ship meant significant down time losses.
11 High Superheater Steam Temperatures
The main boilers of a super tanker which were originally built to fire heavy fuel oil were later converted to fire crude oil as part of its conversion from a trading tanker to stationary use as a Floating Production Storage & Offloading [FPSO] facility. After its relocation from the shipyard to an off-shore location on the West Coast of Africa the boilers were brought into service and fired on crude oil for the first time.
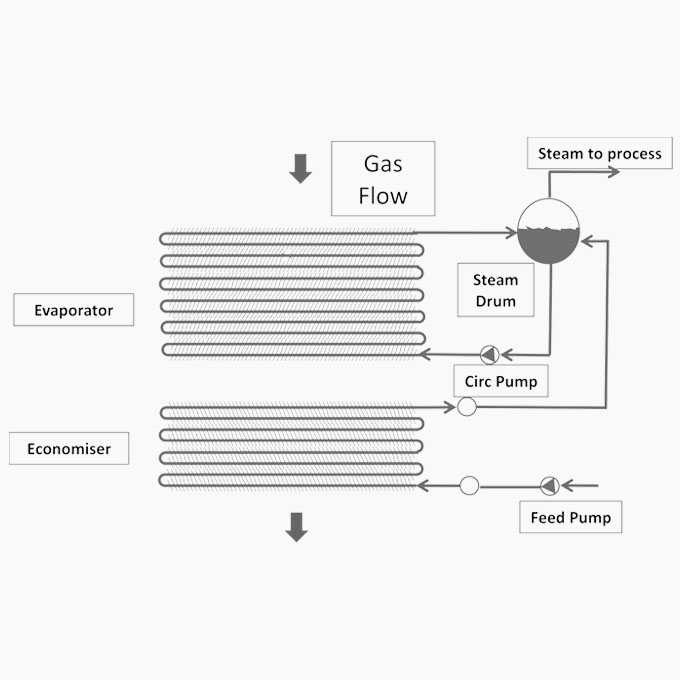
12 HRSG Fin Burn Out
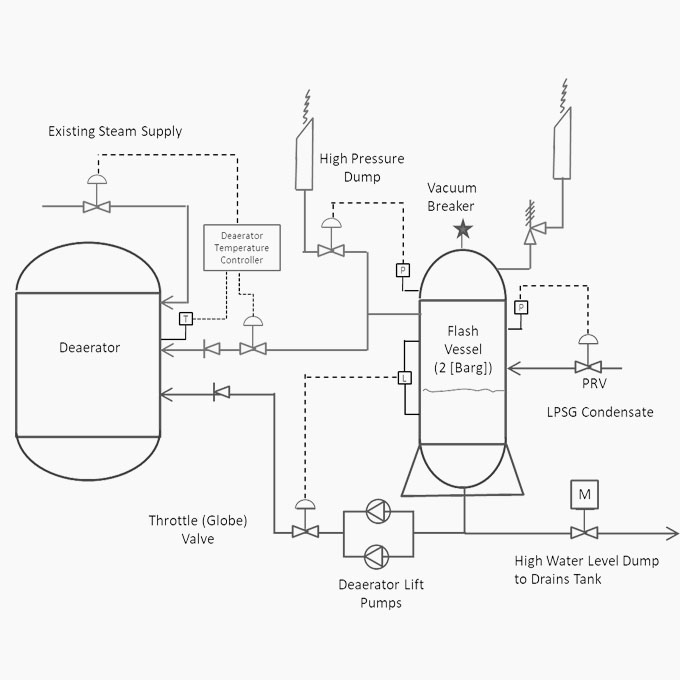
A 20 bar saturated steam Heat Recovery Steam Generator [HRSG] had recently been commissioned at a paper recycling plant. The HRSG was installed behind a 6 MW gas turbine and fitted with a duct burner to boost the boiler’s output. The HRSG was a forced circulation unit fabricated from horizontally oriented spiral wound finned tubes. It had been fitted with two circulation pumps that operated alternatively on a duty / standby basis in accordance with the applicable statutory requirements.
13 Marine Boiler FPSO Oil to Gas Conversion
One of the most significant developments in the oil and gas industry in the seventies and eighties was the coming of age of the super oil tanker. With a statutory practical operating life limited to 25 years, many of these tankers were ultimately retired from service and utilized as Floating Production Storage & Offloading [FPSO] facilities on offshore well heads. To allow these tankers to be redeployed for FPSO operation, their main boilers had to be converted from heavy fuel oil firing to natural gas.
14 Sagging Economizer Tube
The economizer tubes on a 2400 [psi] subcritical coal fired power station boiler were subject to an annual inspection which revealed that the tubes had sagged. This suggested that they had been exposed to excessive operating temperatures. The power station produced 350 MW of electricity and operated on a tight production schedule. Because the economizer tubes formed part of the reheater support system and further tube sagging could damage the reheater elements and shut the plant down for an extended period, this issue required immediate action.
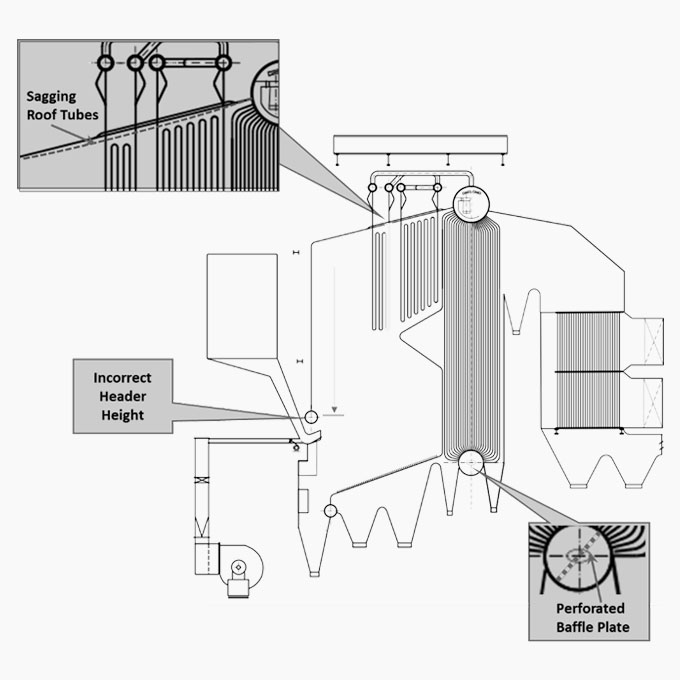
15 Sagging Roof Tubes
The furnace roof tubes in a low-pressure sugar mill grate fired boiler experienced persistent sagging roof tube issues which suggested that the tubes were regularly overheating. The boiler manufacturer insisted that the tubes sagged because of incorrect operational practices, but the operator disagreed. The sugar mill boiler owners had grave concerns that the entire roof would collapse into the furnace if the problem was not quickly addressed. They chose to install a beam above the roof tubes as a temporary measure to address the problem.
16 Superheater Tube Failures
A pulverized coal fired industrial boiler experienced several superheater tube failures about six months after commissioning resulting in several boiler shut downs. The failures were in the platen superheater which hung above the furnace and acted as the first stage of the superheater.
17 Waste Heat Recovery
A refinery identified an opportunity to improve operating efficiency and reduce internal energy consumption by preheating a product stream and extracting heat from the tail end of a cat cracker exhaust stream. Design Boiler [DB] designed a complete heat recovery system that required minimal draught plant modifications and maintain low fan power requirements. Following a comprehensive thermal design analysis, a full set of certified fabrication drawings were prepared for use by a third party contractor for manufacture.
18 Wood Fired Boiler - High Particulate Emissions
A medium pressure wood waste fired boiler was experiencing major combustion problems. The plant was producing compressed wood sheeting and door panels, using processed wood fibers. The boiler was fired on various process waste streams including saw dust. The boiler produced 65,000 [lbm/hr] of 600 psi saturated steam which was predominantly used by the process for stripping fiber from the wood.