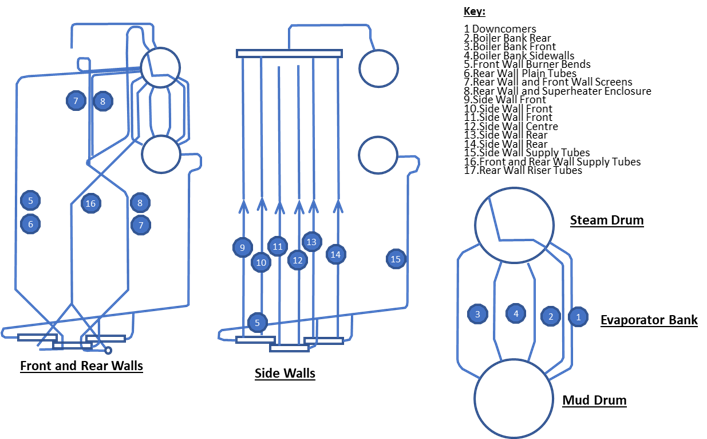
CAPABILITIES
Boiler Circulation Root Cause Analysis

A well-designed boiler circulation system is usually very robust and able to withstand a wide range of operational upset conditions. Conversely a poorly designed system may exhibit a multitude of operational problems such as: frequent tube failures, drum level control instability, superheater tube failures and turbine fouling.
Design Boiler has many years experience using boiler circulation modelling conduct root cause analysis on boiler circulation problems. Boiler circulation is a highly specialised field and in our experience a significant number of industrial boilers that are in service have never been subjected to a proper circulation analysis. As such operational problems in this area are surprisingly common. All too frequently these conditions are incorrectly attributed to poor water treatment which computer modelling is likely to identify as a circulation defect.
With its boiler circulation computer modelling capability, Design Boiler is able to identify relevant circulation parameters of interest that assist in the diagnosis of defective circulation.
A typical boiler circulation root cause analysis would involve the following activities:
SCENARIO:
A steam raising plant experiences typical defective circulation symptoms such as persistent furnace tube failures, and poor steam drum level control.
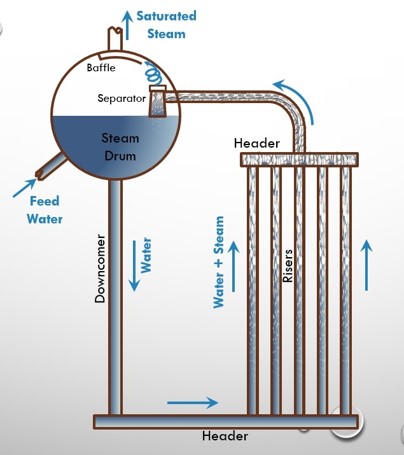
METHODOLOGY:
Site Visit:
- Collate operating data and OEM design performance parameters.
Boiler Circulation Modelling:
- Configure boiler computer model to simulate internal heat transfer with differing furnace fouling conditions.
- Model circulation under different load cases reflecting variations in furnace heat absorption.
- Identify critical load cases indicating low circulating velocity. Relate these to symptoms observed on site which may be poor drum level control or persistent tube failures. Both of these problems can be caused by poor downcomer stability. In that case the flow in steam drum riser tubes reverses uncontrollably.
Case studies demonstrating these analytical capabilities may be found here and here. An additional case study relating to downcomer stability can be found here.