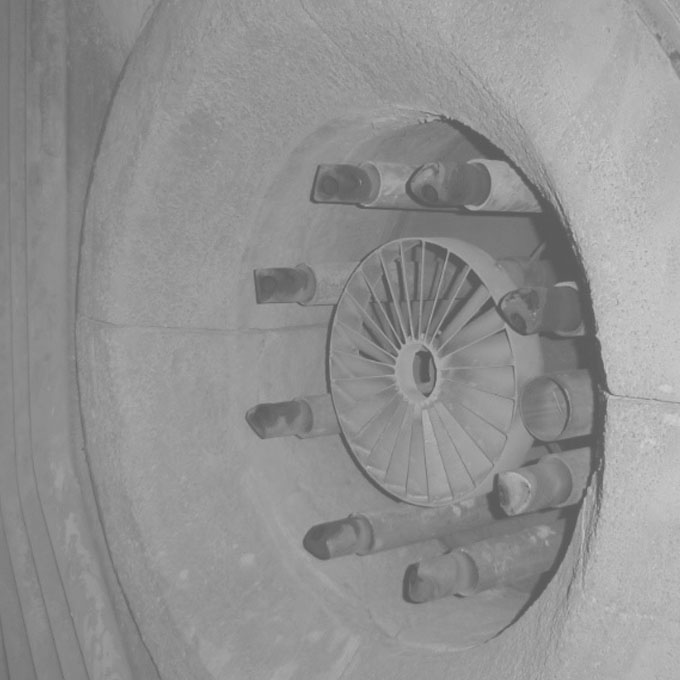
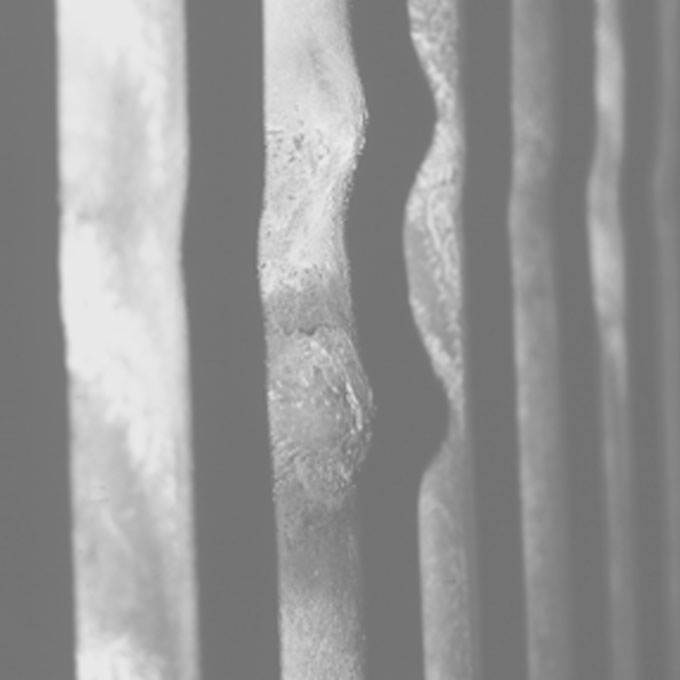
01 Airheater Metal Fire | Biomass Fuel
Design Boiler was engaged to investigate the cause of a metal fire in a wood fired boiler that had destroyed its airheater. The fire effectively shut the plant down for over 12 months. A metal fire is one of the most extreme operational hazards likely to be encountered within a boiler. Once initiated they can be extremely difficulty to extinguish and they have the capacity to destroy an entire boiler in a very short period of time.
02 Biomass | Hotwater Boiler Design
A small timber processing plant needed to reduce energy costs. Sawdust, which was a site waste product, was available as a free source of fuel. If this could be burned to heat hot water, it would displace Natural Gas, and reduce the site’s energy costs.
03 Biomass | High Particulate Emission & Load Limiting
A biofuel plant had purchased a 45 T/hr boiler from a leading boiler manufacturer to generate electricity through a small steam turbine at their production facility. However, the plant owners believed that the boiler was unable to achieve its Maximum Continuous Rating (MCR) and that its particulate emissions exceeded statutory limits. Design Boiler was engaged by the boiler manufacturer to provide an independent opinion.
04 Biomass | Thermal Oil Economiser
A medium sized timber processing plant was looking to expand its operation by introducing a new product. The production expansion was going to impose a significant additional burden on the site heat plant capacity. The site was remote with no reticulated gas supply available and the cheapest alternative fuel source was a bulk LPG which would have to be trucked in. A cost benefit analysis indicated that the cost of providing LPG as a substitute fuel source would render the proposed production expansion unviable.
05 Boiler Internal Corrosion
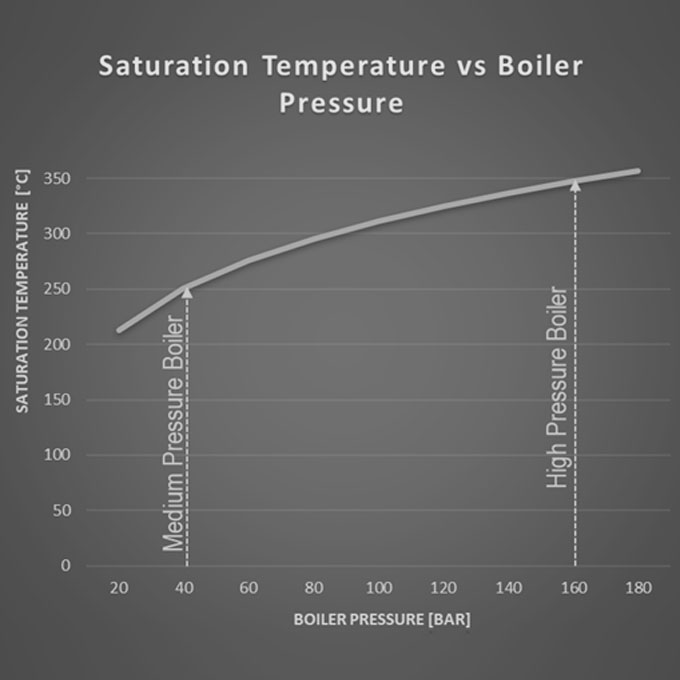
A relatively new high pressure boiler was installed on the deck of an oil tanker that had been recently converted to a Floating Production Storage & Offloading [FPSO] facility. The 110 [TPH] boiler operated at around 65 [Bar] and produced 510 [°C] superheated steam. Shortly after its 12 month warranty period had elapsed, and following a statutory boiler inspection, significant corrosion damage throughout the entire boiler was discovered.
06 Boiler Explosion
A small low pressure (8 [Bar]) waste heat recovery boiler installed at the back end of the main propulsion engine of a trading ship exploded at sea shortly after the boiler had been serviced. The explosion caused extensive damage to the ship and prevented it from sailing under its own power. It was towed to a nearby port where it was laid up for over 12 months for repair.
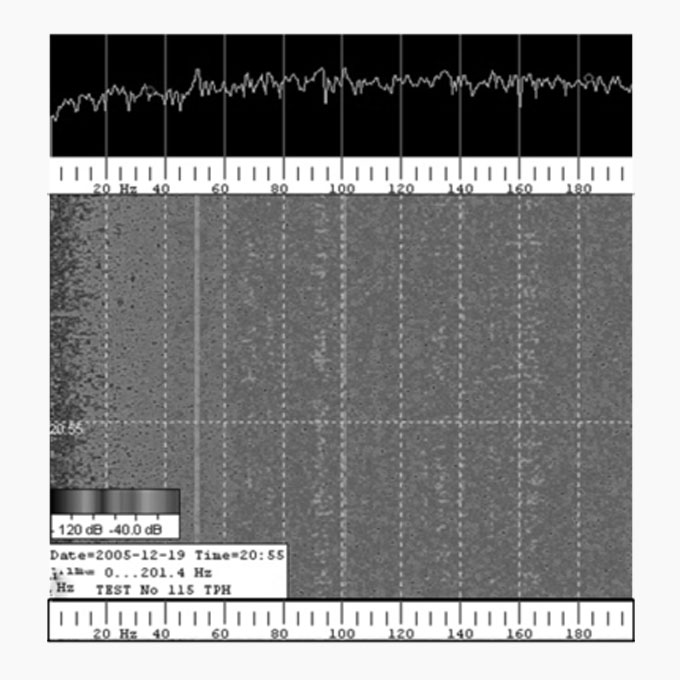
07 Boiler Vibration
A natural gas fired high pressure boiler recently installed in a gas refinery had been experiencing major vibration problems which limited the boiler’s ability to achieve its maximum rated output. As was typical of boiler vibration issues, the problem exhibited a threshold load below which the vibration did not occur.
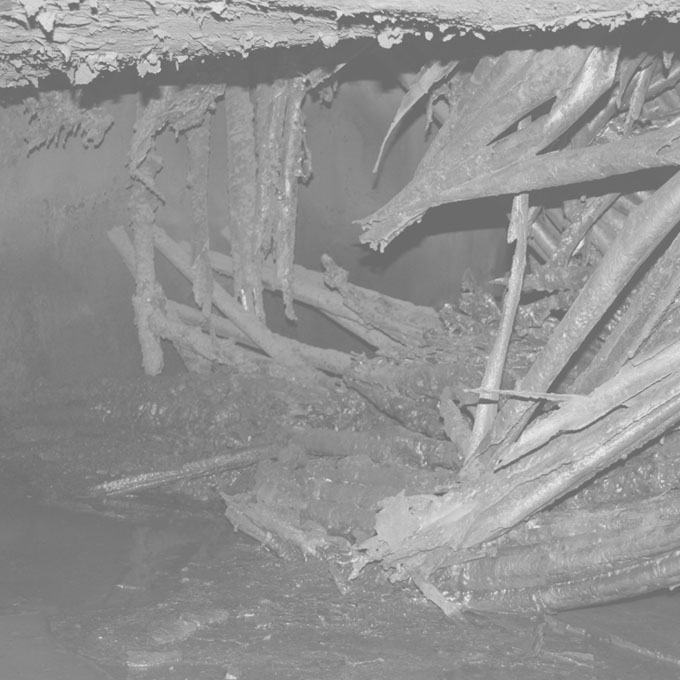
08 Defective Boiler Circulation
A 600,000 [lbm/hr] high pressure pulverized coal boiler operating at a steelworks experienced persistent furnace wall tube blistering within 6 months of being first commissioned. After 3 months some of the blistered tubes began to fail causing frequent forced plant outages and expensive production losses. The boiler manufacturer blamed poor water treatment, pointing to the presence of a thin scale detected on the inside surface of the tube within the zone of the failures. A new water treatment chemical supplier was engaged but despite an intense focus on optimizing water chemistry over an additional 12-month period the problem persisted.
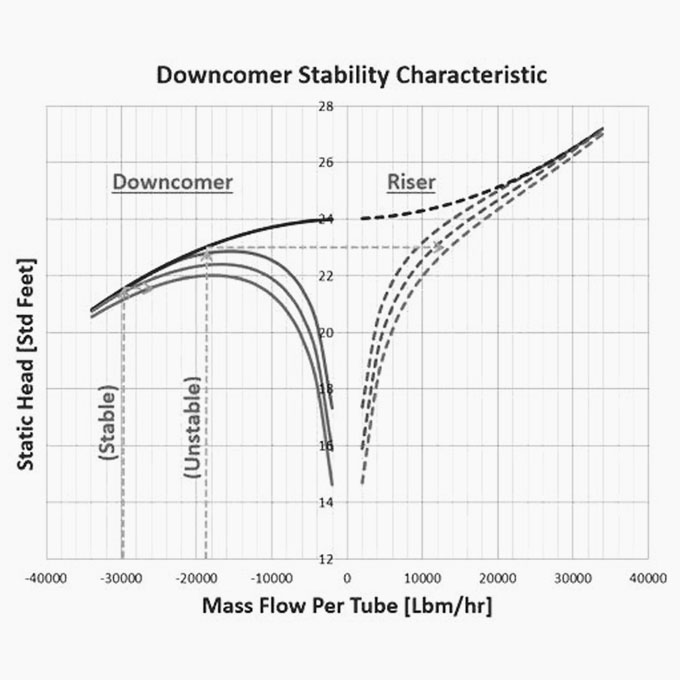
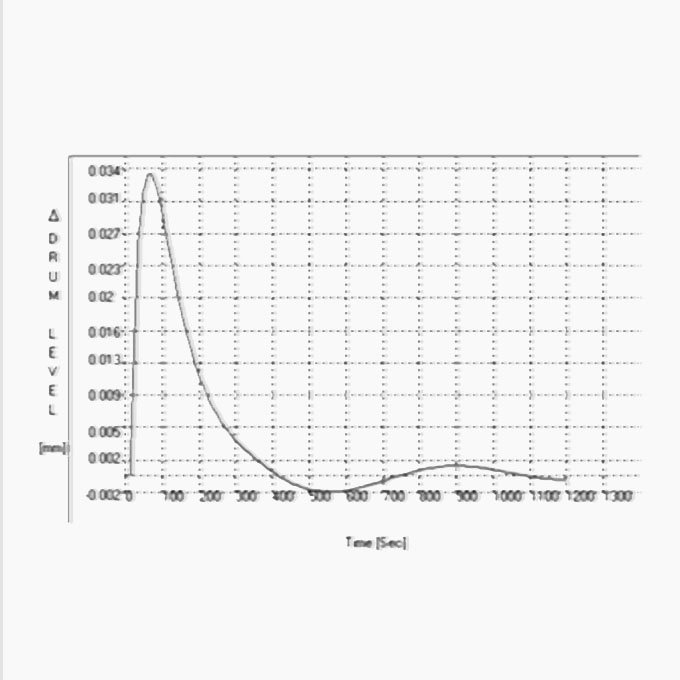
09 Downcomer Instability
The commissioning of a new 250 [TPH] high pressure boiler could not be completed because of ongoing problems with the drum level control system. The boiler also exhibited a number of other unusual problems including a significant variation in drum level between the left and right hand side of the drum. The boiler was a pulverized coal fired natural circulating bi drum unit producing 62 [Bar] steam at [470] °C. It was fitted with a three-element drum level control system but irrespective of whatever control settings were made the drum level would initially exhibit a measure of stability only to become erratic and uncontrollable during subsequent operation.
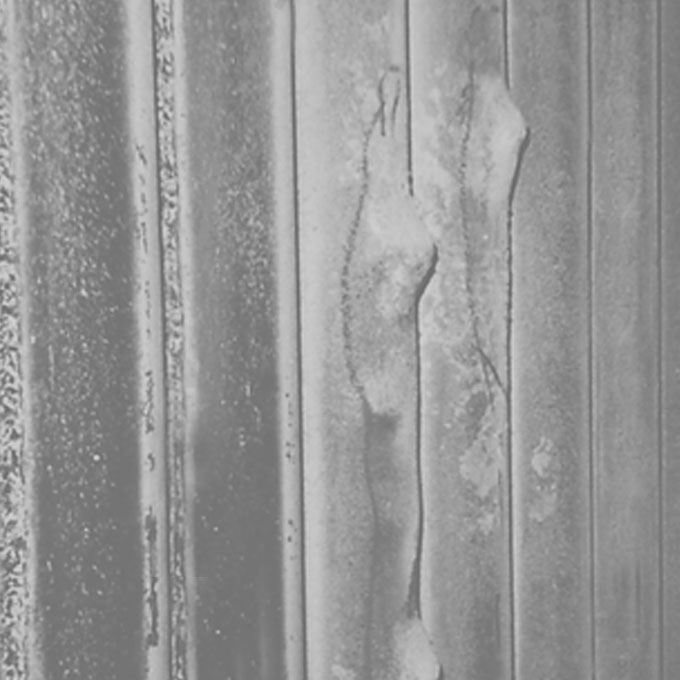
10 Economiser Metal Fire
An exhaust gas boiler fitted in the uptake of a trading VLCC motor tanker was destroyed beyond repair by a metal fire, stranding the fully laden vessel in a foreign port. The high value of the cargo and the size of the ship meant significant down time losses.
11 High Superheater Steam Temperatures
The main boilers of a super tanker which were originally built to fire heavy fuel oil were later converted to fire crude oil as part of its conversion from a trading tanker to stationary use as a Floating Production Storage & Offloading [FPSO] facility. After its relocation from the shipyard to an off-shore location on the West Coast of Africa the boilers were brought into service and fired on crude oil for the first time.
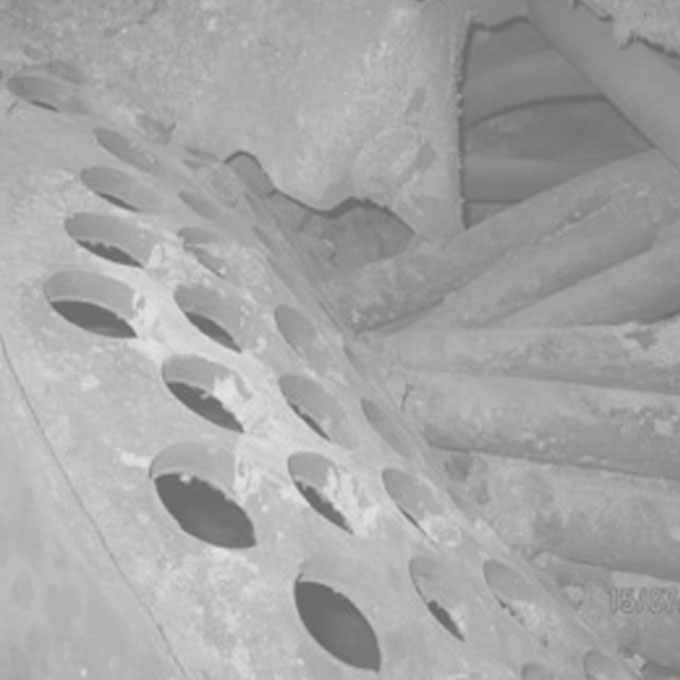
12 HRSG Fin Burn Out
A 20 bar saturated steam Heat Recovery Steam Generator [HRSG] had recently been commissioned at a paper recycling plant. The HRSG was installed behind a 6 MW gas turbine and fitted with a duct burner to boost the boiler’s output. The HRSG was a forced circulation unit fabricated from horizontally oriented spiral wound finned tubes. It had been fitted with two circulation pumps that operated alternatively on a duty / standby basis in accordance with the applicable statutory requirements.
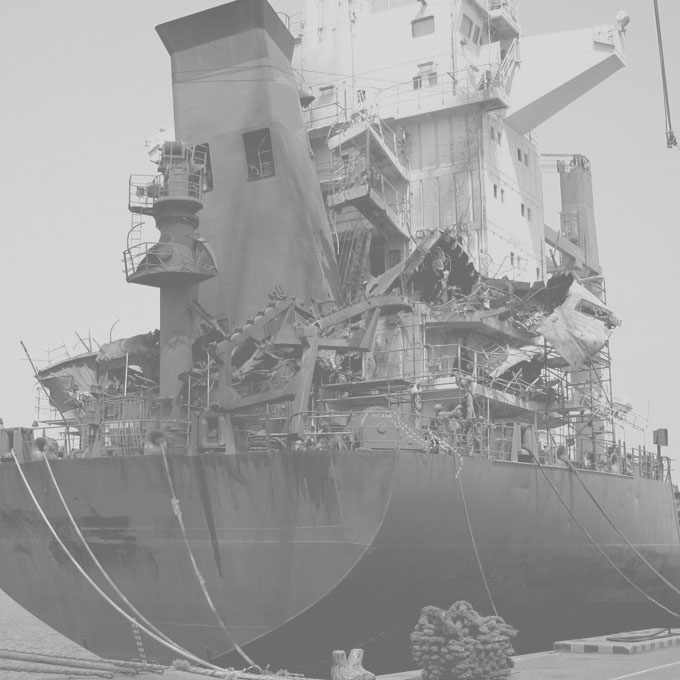
13 Marine Boiler FPSO Oil to Gas Conversion
One of the most significant developments in the oil and gas industry in the seventies and eighties was the coming of age of the super oil tanker. With a statutory practical operating life limited to 25 years, many of these tankers were ultimately retired from service and utilized as Floating Production Storage & Offloading [FPSO] facilities on offshore well heads. To allow these tankers to be redeployed for FPSO operation, their main boilers had to be converted from heavy fuel oil firing to natural gas.
14 Sagging Economizer Tube
The economizer tubes on a 2400 [psi] subcritical coal fired power station boiler were subject to an annual inspection which revealed that the tubes had sagged. This suggested that they had been exposed to excessive operating temperatures. The power station produced 350 MW of electricity and operated on a tight production schedule. Because the economizer tubes formed part of the reheater support system and further tube sagging could damage the reheater elements and shut the plant down for an extended period, this issue required immediate action.
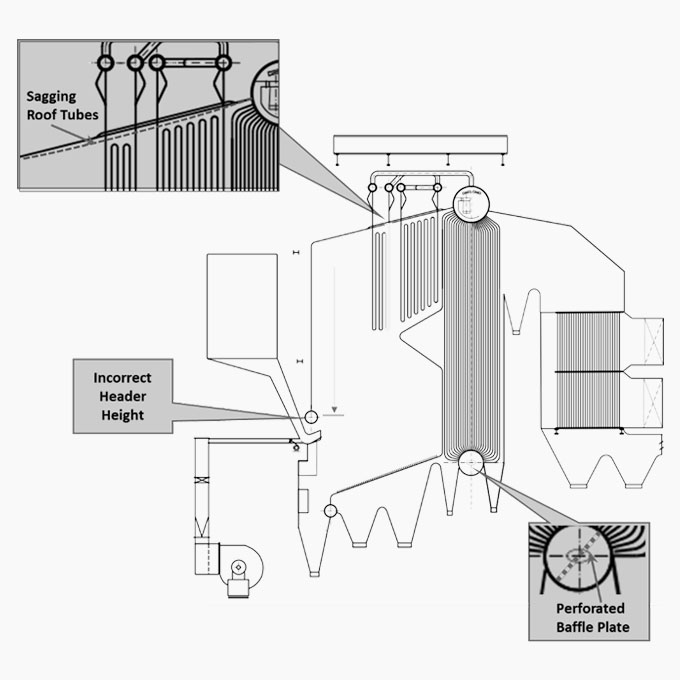
15 Sagging Roof Tubes
The furnace roof tubes in a low-pressure sugar mill grate fired boiler experienced persistent sagging roof tube issues which suggested that the tubes were regularly overheating. The boiler manufacturer insisted that the tubes sagged because of incorrect operational practices, but the operator disagreed. The sugar mill boiler owners had grave concerns that the entire roof would collapse into the furnace if the problem was not quickly addressed. They chose to install a beam above the roof tubes as a temporary measure to address the problem.
16 Superheater Tube Failures
A pulverized coal fired industrial boiler experienced several superheater tube failures about six months after commissioning resulting in several boiler shut downs. The failures were in the platen superheater which hung above the furnace and acted as the first stage of the superheater.
17 Waste Heat Recovery
A refinery identified an opportunity to improve operating efficiency and reduce internal energy consumption by preheating a product stream and extracting heat from the tail end of a cat cracker exhaust stream. Design Boiler [DB] designed a complete heat recovery system that required minimal draught plant modifications and maintain low fan power requirements. Following a comprehensive thermal design analysis, a full set of certified fabrication drawings were prepared for use by a third party contractor for manufacture.
18 Wood Fired Boiler - High Particulate Emissions
A medium pressure wood waste fired boiler was experiencing major combustion problems. The plant was producing compressed wood sheeting and door panels, using processed wood fibers. The boiler was fired on various process waste streams including saw dust. The boiler produced 65,000 [lbm/hr] of 600 psi saturated steam which was predominantly used by the process for stripping fiber from the wood.
Boiler Forensic Analysis & Expert Witness Services
Defective steam generation equipment may impose significant financial losses on plant owners which can justify recovery action. Often the defects causing these losses could have been avoided if the boiler design had conformed with best practice guidelines. Conversely, there are circumstances where poor steam plant availability or defective boiler performance that is caused by maintenance and/or difficult operational issues is incorrectly attributed to boiler design.
Boiler Performance Analysis & Computer Modelling
Boiler heat transfer is significantly different to that of a typical industrial process and needs to be analyzed and modelled using purpose-built software. Our extensive range of boiler performance modelling software includes software packages that model the entire gas side process within almost any boiler.
Boiler & Superheater Tube Root Cause Failure Analysis
The evaporative surfaces of a boiler should achieve an indefinite operating life provided the circulation system is correctly designed and the water treatment management is satisfactory. However tube failures in furnaces and evaporative surfaces are surprisingly common and can force boiler plant to be shut down unexpectedly.
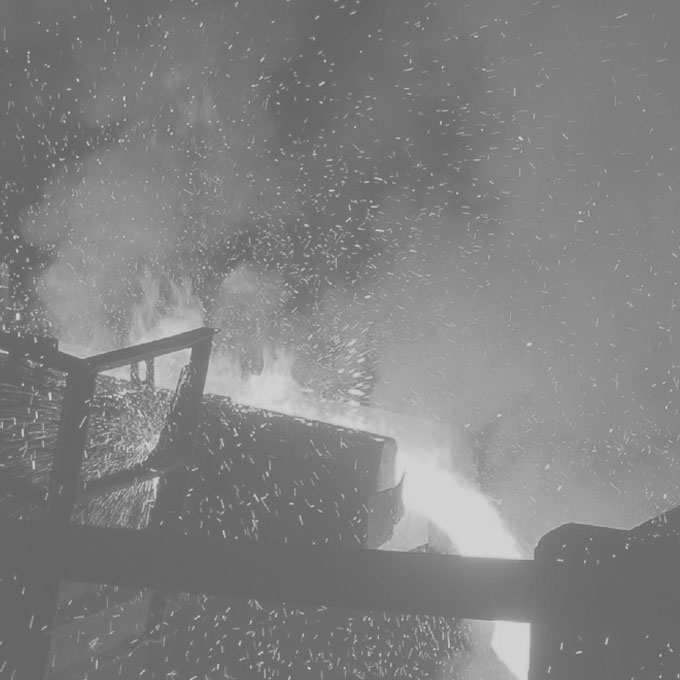
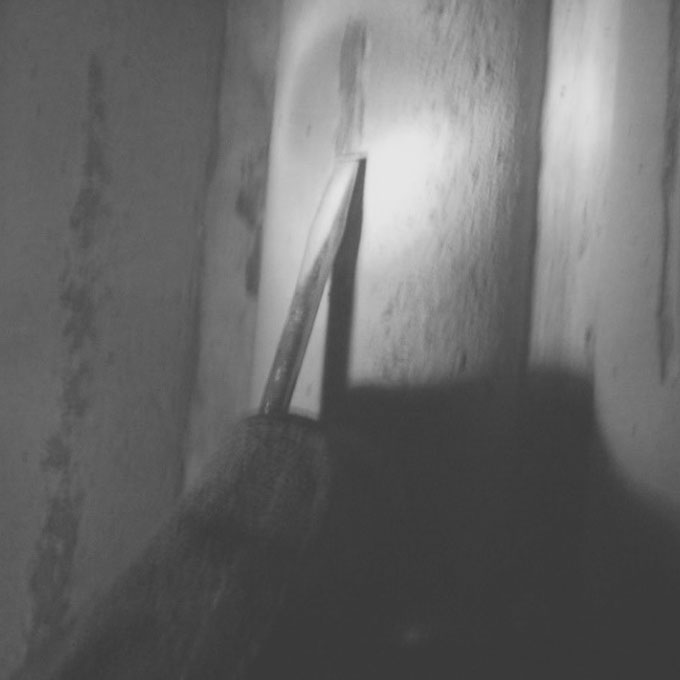
Boiler Catastrophic Fire Investigations
Metal fires within boilers can be extremely dangerous and may cause extensive catastrophic damage to the boiler and its auxiliary equipment. This is because the fire which often develops at the cooler, back end of the boiler can reach an intensity that causes the plain boiler tubes or tube fins to combust and burn. Once almost exclusively associated with oil fired boilers, the increased combustion of biomass fuel streams has seen an increasing number of metal fires beginning to occur in solid fuel boiler applications.
Boiler Explosion Investigations
In the early days of steam power, boiler explosions were common place. In fact before 1780 boilers rarely operated above 1 or 2 [psi]. This was a limit intended to reduce the frequent number of boiler explosions that were occurring at that time. More advanced higher steam pressure designs did not enter commercial production until after 1800, by which time the concept of “strong steam “ was coined to describe a boiler operating at or above 30 [psi].
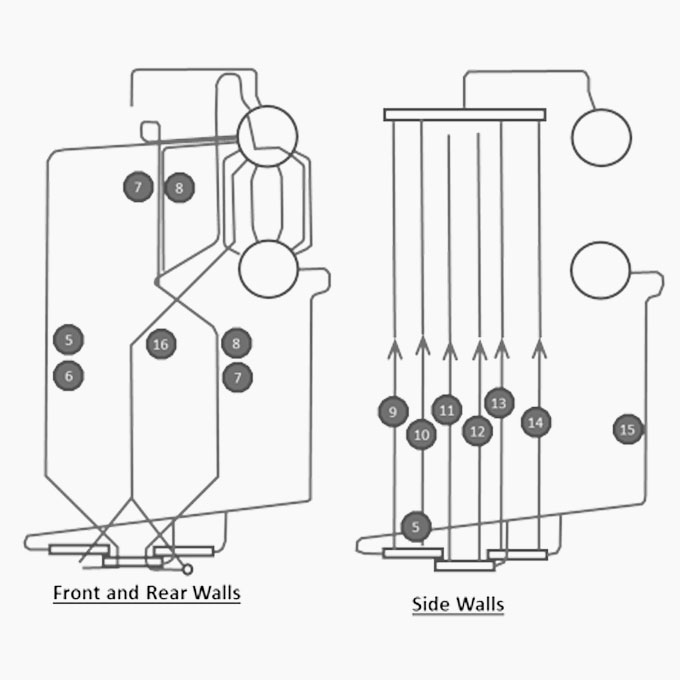
Boiler Circulation Analysis
A well-designed boiler circulation system is usually very robust and able to withstand a wide range of operational upset conditions. Conversely a poorly designed system may exhibit a multitude of operational problems such as: frequent tube failures, drum level control instability, superheater tube failures and turbine fouling.
Boiler Combustion & Emission Optimisation
Design Boiler has been addressing poor combustion and emission problems on biomass / wood waste boilers for many years. Often high emissions are a direct result of poor combustion and this that overloads the dust collector by producing an excessively high inlet dust burden.
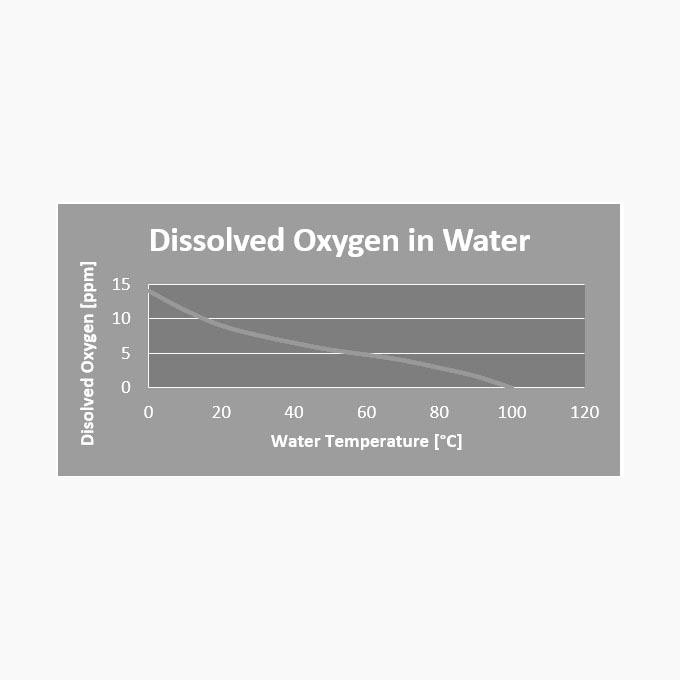
Boiler Corrosion Investigation
The two most common causes of internal boiler corrosion are: a) Oxygen attack; or b) Acid attack following chemical cleaning. Their can be other types of corrosive attacks on the tubes such as caustic gouging which is related to hydrogen embrittlement, but these are often associated with other factors such as circulation deficiencies.
Boiler Dynamic Analysis
Design Boiler have developed software that is able to simulate the dynamic response of a boiler control system to rapid changes in boiler load. Sudden changes in steam demand can cause rapid rises in steam pressure that may lift safety valves. The lifting of safety valves may then lead to a sudden drop in boiler pressure causing drum level instability and this can trip the boiler on high steam drum water level. The ability to recover from this type of upset condition depends on a boiler’s control settings, it’s thermal inertia, steam drum size and combustion system capacity.
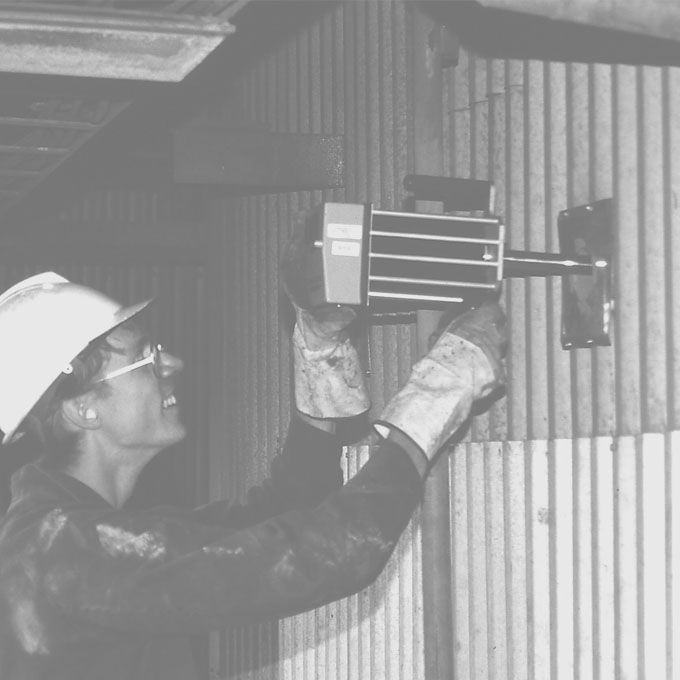
Boiler Plant Testing & Diagnostics
Many boiler plant problems can be difficult to diagnose and fix. Boilers operate under extreme conditions and can sometimes require experienced and specialized expertise to resolve challenging operational problems that may be encountered. Design Boiler is able to mobilize these specialized boiler plant testing and diagnostic services to most global locations. Our personnel are certified for confined space entry and have been trained to internationally recognised BOSIET & HUET systems for immediate off shore mobilization.
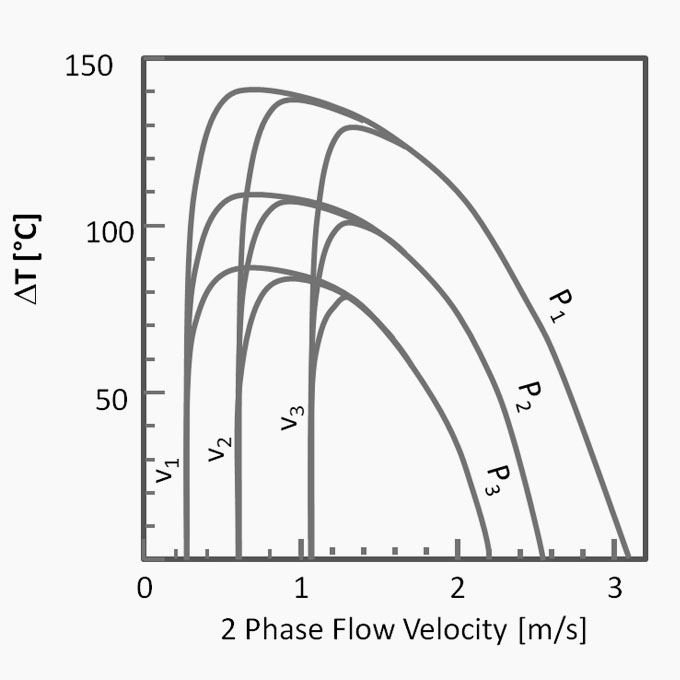
Boiler Tube Bank and Furnace Vibration
Vibration can impose major restrictions on a boiler’s steam generating capacity and inflict significant long term structural damage. Typically vibrations will occur above a distinct threshold load or within a very narrow operating load range. If the boiler is operated above or within this load profile for extended periods, it can sustain substantial damage.
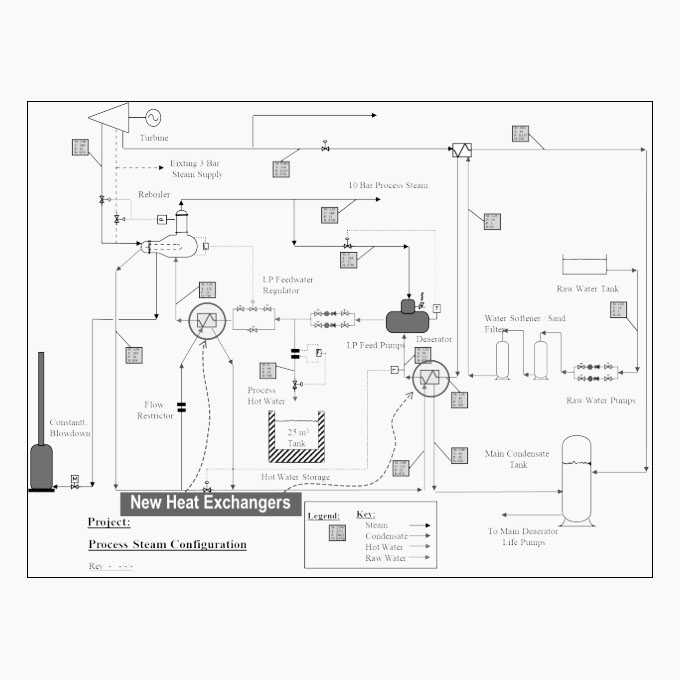
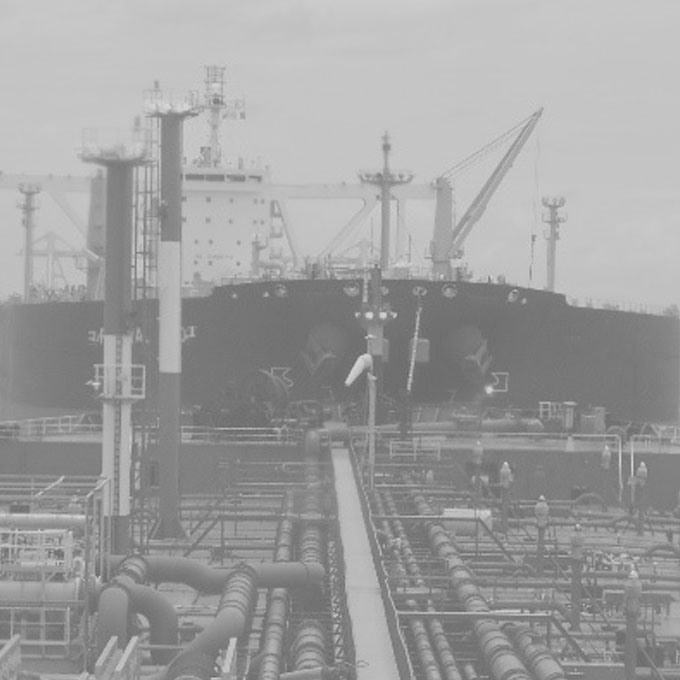
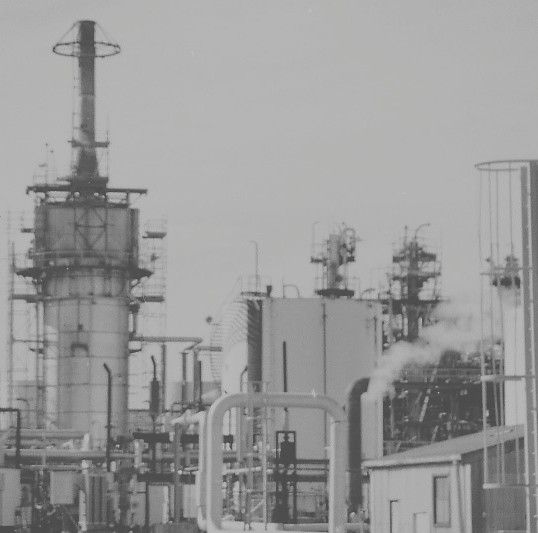
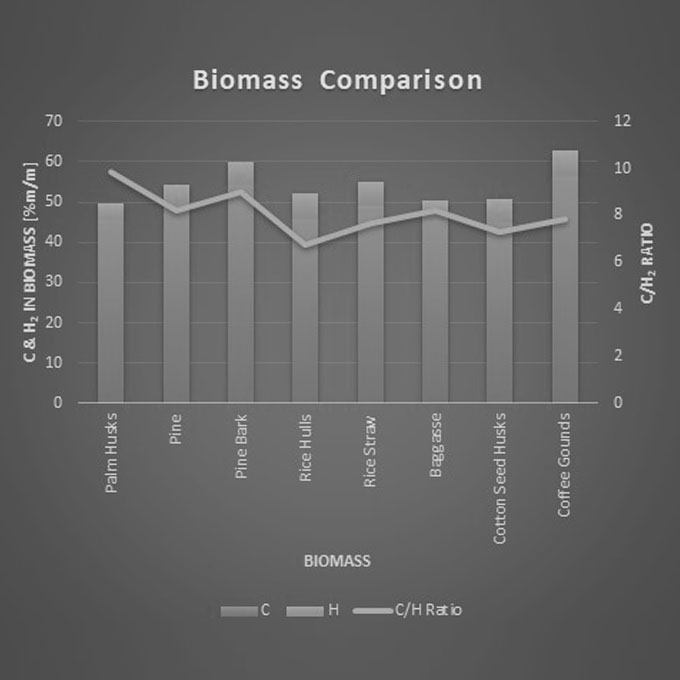
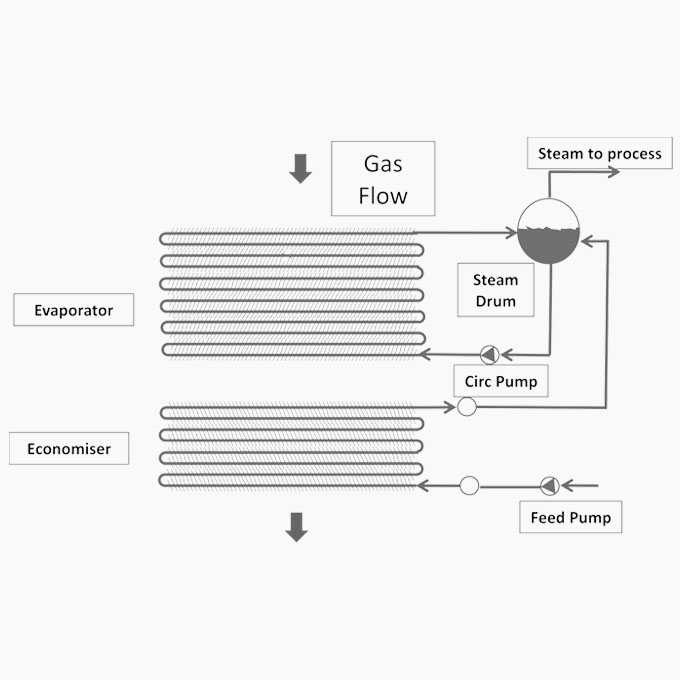
Cogeneration / Combined Heat & Power [CHP]
The utilization of waste heat in industry for the production of steam to generate electricity has grown steadily since the 1970’s. Rising fuel and electricity costs along with increasing concerns about environmental emissions have seen a gradual rise in the number of cogeneration and combined heat & power [CHP] plants globally.
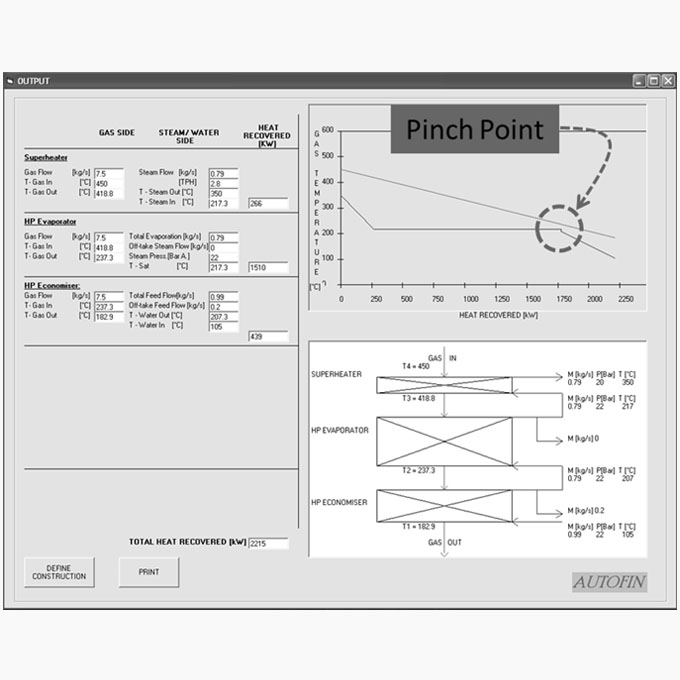
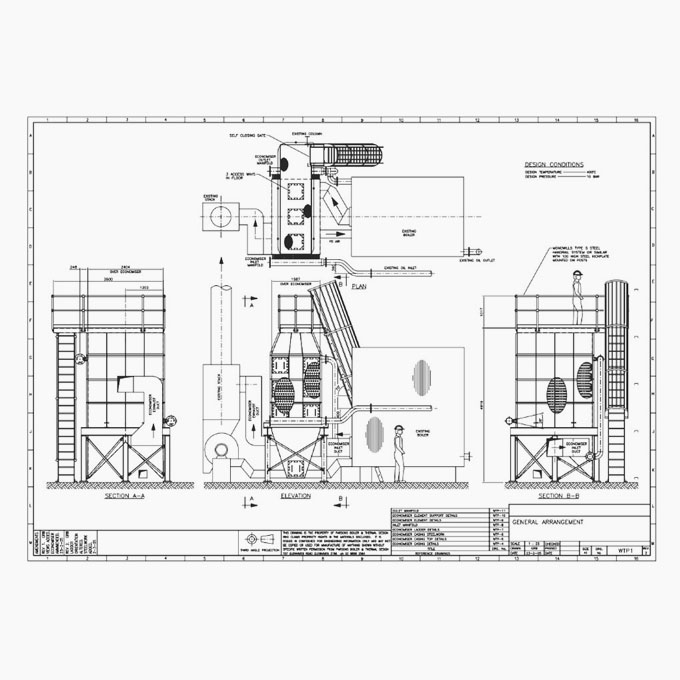
Heat Recovery Steam Generator [HRSG] Design & Diagnostics
Design Boiler has been involved in the design and the diagnostics of problems with HRSG’s for many years. Our technology has also been utilized to verify the suitability of deck mounted HRSGs in key offshore marine installations and to design HRSG’s for industrial co-generation plants.
Oil to Gas Firing Conversion
Design Boiler is skilled and experienced in undertaking the necessary computer modelling , design work and field testing required for converting oil fired boilers to gas firing. Typically an oil fired Marine boiler destined for operation on an off shore Floating Production Storage & Offloading [FPSO] platform will need conversion from oil to gas firing. Design Boiler will receive a request to carry out the necessary redesign of the boiler and prepare the required documentation for submission to the relevant marine class authority ( ABS, Lloyds, DNV etc.)
Pulverized Coal Firing Systems
Pulverized coal [PC] firing can pose unique challenges such as poor grinding performance, high carbon in ash, slagging problems and excessively high furnace heat fluxes due to combustion related issues. There are many different pulverizing systems and each has its own specific requirements.
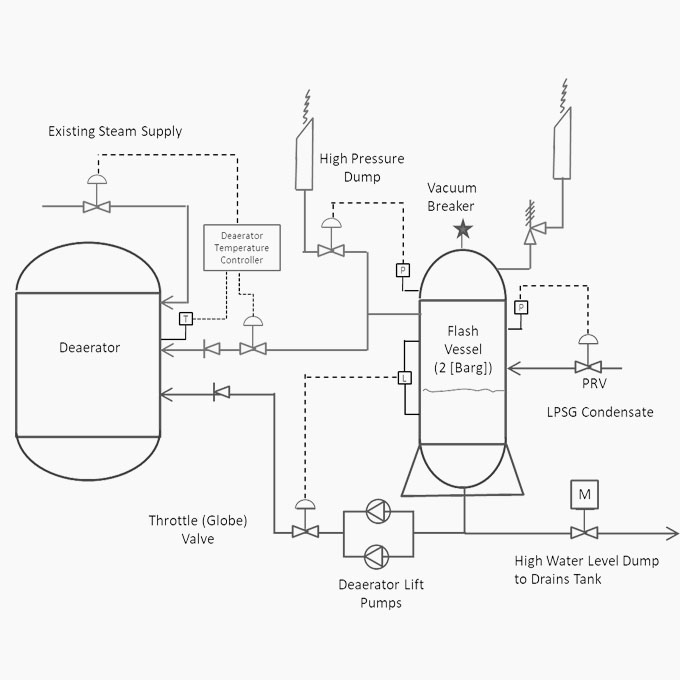
Steam Cycle Optimization
A poorly designed or problematic steam cycle can impact on overall plant efficiency and significantly increase energy costs. High flash steam losses and excessive condensate makeup are all symptoms of a badly balanced steam cycle which can have detrimental effects on the performance of downstream appliances such as deaerators and steam turbines.
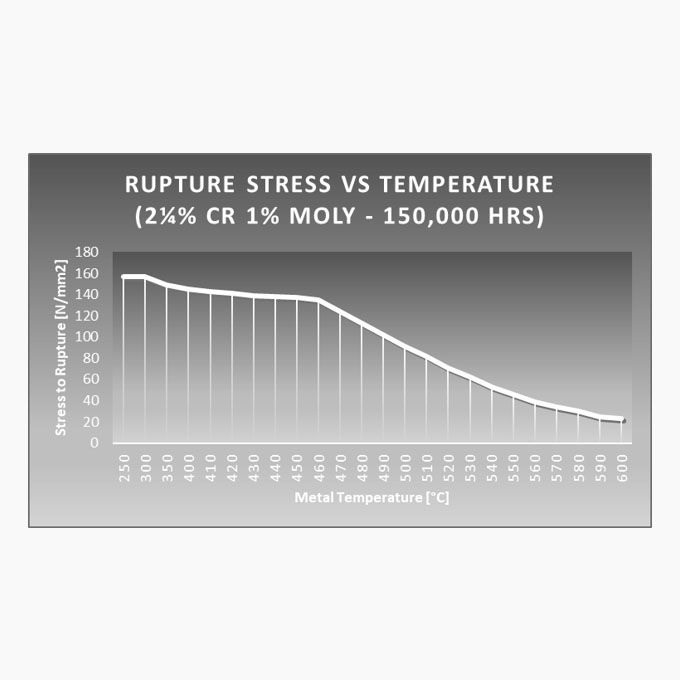
Superheater Design
Design Boiler has the necessary computer modelling resources and expertise to determine metal temperatures for the selection of tube materials to achieve an acceptable design life. Superheaters operate within a very arduous environment and are often designed at the extreme end of their tube’s metallurgical limits. As well as being the first receiver of the hottest flue gases generated within the furnace, they are constantly subject to direct radiation from the combustion process. Most boiler design standards (ASME, BS, ISO, Lloyds, ABS etc) require the superheater to be designed to achieve a minimum design life in terms of operating hours. For example, BS & ISO standards require the superheater to be designed for a minimum of 100,000 hours. This requires the likely metal temperatures that the superheater will be subject to during normal operation to be determined and that an appropriate tube material is selected to withstand those temperatures.
Waste Heat Recovery Systems
It was the Arab Oil Embargo of the 1970’s that forced industry to become more energy efficient and invest in low grade heat recovery systems. Following this global event it was soon realized that the cost saving engineering strategies utilized in the design of waste heat recovery systems also produced significant benefits for the environment.
















![Cogeneration / Combined Heat & Power [CHP]](https://www.designboiler.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/04/C-12.jpg)
![Heat Recovery Steam Generator [HRSG] Design & Diagnostics](https://www.designboiler.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/04/C-13.jpg)